- Overview
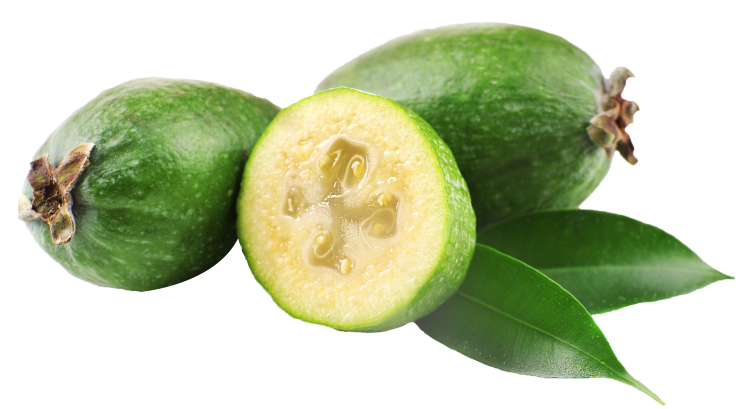
Pineapple Guava/Fieoja Tree in a 3 Gallon Container. The feijoa, or Pineapple Guava is native to extreme southern Brazil, northern Argentina, western Paraguay and Uruguay where it is common in the mountains. Is widely planted as a hedge, specimen or more ornately as an specimen and can if unpruned can reach heights of 15 feet tall and 15 feet wide in as many years. Pineapple Guava is used for two distinctly different purposes: for its flowers and for its fruits. There are few landscape plants that can be used for both, but its brilliant flowers, bright pink and red reaching 1.5 inches in diameter generally astound passerby’s. Its fruits are sweet and the taste resembles a cross between pineapple and guava. Fruits range in size from ¾ inch to 3 ½ inches long and are soft and yellow when ripe. Another useful purpose for the Feijoa is that it is very tolerant of salt, though this decreases fruit yield and causes it to produce fewer flowers. The leaves are leathery, dark green on top and a pale gray on the underside. The plant is remarkably disease and insect resistant, which makes landscaped areas easier to maintain. Makes a great edible hedge
Description
Origin and Distribution
Varieties
Pollination
Climate
Soil
Propagation
Culture
Season and Yield
Keeping Quality
Pests and Diseases
Food Uses
Description
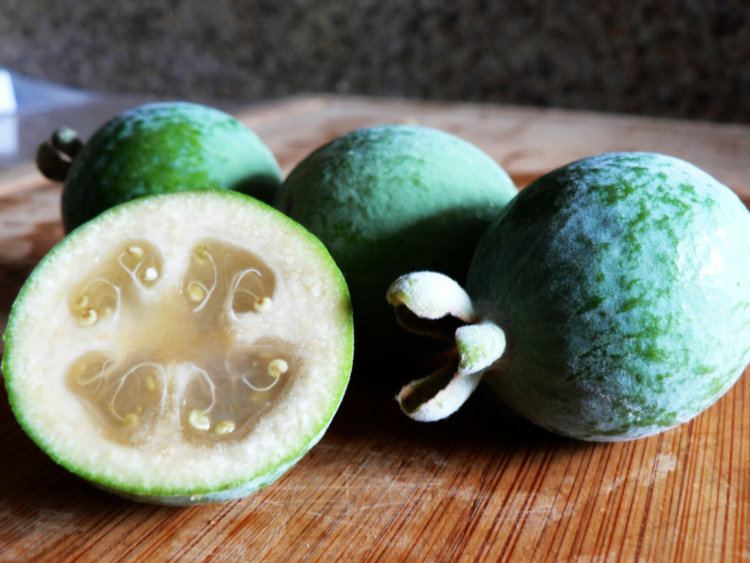
The plant is a bushy shrub 3 to 20 ft (0.9-6 m) or more in height with pale gray bark; the spreading branches swollen at the nodes and white-hairy when young. The evergreen, opposite, short-petioled, bluntly elliptical leaves are thick, leathery, 1 1/8 to 2 1/2 in (2.8-6.25 cm) long, 5/8 to 1 1/8 in (1.6-2.8 cm) wide; smooth and glossy on the upper surface, finely veiny and silvery-hairy beneath. Conspicuous, bisexual flowers, 1 1/2 in (4 cm) wide, borne singly or in clusters, have 4 fleshy, oval, concave petals, white outside, purplish-red inside; 5/8 to 3/4 in (1.6-2 cm) long, and a cluster of numerous, erect, purple stamens with round, golden-yellow anthers. The fruit is oblong or ovoid or slightly pear-shaped, 1-1 1/2 to 2 1/2 in (4-6 cm) long and 1 1/8 to 2 in (2.8-5 cm) wide, with the persistent calyx segments adhering to the apex. The thin skin is coated with a "bloom" of fine whitish hairs until maturity, when it remains dull-green or yellow-green, sometimes with a red or orange blush. The fruit emits a strong long-lasting perfume, even before it is fully ripe. The thick, white, granular, watery flesh and the translucent central pulp enclosing the seeds are sweet or subacid, suggesting a combination of pineapple and guava or pineapple and strawberry in flavor. There are usually 20 to 40, occasionally as many as 100, very small, oblong seeds hardly noticeable when the fruit is eaten.
Origin and Distribution
The feijoa is native to extreme southern Brazil, northern Argentina, western Paraguay and Uruguay where it is common wild in the mountains. It is believed that the plant was first grown in Europe by M. de Wette in Switzerland and, a little later, about 1887, it was known to be in the Botanic Garden at Basle. In 1890, the renowned French botanist and horticulturist, Dr. Edouard Andre, brought an air-layered plant from La Plata, Brazil and planted it in his garden on the Riviera. It fruited in 1897. Dr. Andre published a description with color plates of the leaves, flowers and fruit, in the Revue Horticole in 1898, praising the fruit and recommending cultivation in southern France and all around the Mediterranean area.
A nurseryman in Lyons distributed air-layers from the Andre plant in 1899 and many were planted on the Riviera, some in Italy and Spain and some in greenhouses further north. That same year, the prominent nurserymen, Besson Freres, obtained seeds from Montevideo and raised thousands of plants which were widely sold and proved to be of a different type than Dr. Andre's plant. Seeds were imported by one or two other French nurserymen, and then, in 1901, seedlings from Dr. Andre's plant were obtained by Dr. F. Franceschi of Santa Barbara, California, from M. Naudin of Antibes. These were planted at several different California locations. In 1903, Dr. Franceschi acquired, through F. Morel of Lyons, several air layers from Dr. Andre's plant. He planted 1 or 2 at Santa Barbara and most of the rest were sent to Florida. The plant did not succeed in southern Florida but became quite popular in northern Florida, primarily as an ornamental and particularly as a clipped hedge. Dr. Henry Nehrling had two plants growing well in a shed in half-shade at Gotha in central Florida, in 1911. They flowered and fruited but the fruit dropped before maturity and rotted quickly. In recent years, the cultivar 'Coolidge', vegetatively propagated, has borne well in Florida. In California, the feijoa is grown in a limited way for its fruit, especially in cool coastal locations, mainly around San Francisco. At the Experimental Station in Honolulu a plant flourished for 15 years without bearing fruit. Later plantings have succeeded at higher elevations.
The feijoa is sometimes cultivated in the highlands of Chile and other South American countries and in the Caribbean area. Jamaica received a few plants from California in 1912 and planted them at various altitudes. I have seen occasional plants on roadsides and in private gardens in the Bahamas, but they do not fruit and often fail to flower. In southern India, the feijoa is grown for its fruit in home gardens at temperate elevations–about 3,500 ft (1,067 m).
Nowhere has the feijoa received more attention than in New Zealand. An Auckland nurseryman introduced 3 cultivars from Australia–'Coolidge', 'Choiceana', and 'Superba'–about 1908. They remained little known until 1930 when the feijoa was advertised as an ornamental plant. Later, after improvement by selection and naming of types with large, superior fruits and their vegetative propagation, small commercial plantings were made in citrus-growing areas of the North Island. The New Zealand Feijoa Growers' Association was formed in 1983 and some fruit is being exported to the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, Netherlands, France and Japan. New Zealanders also plant the feijoa as a windbreak around wind-sensitive crops. It is planted as an ornamental and for its fruit in southern Africa. Following WW II, feijoa plantations were established in North Africa, the Caucasian region of southern Russia, as well as in Sicily, Portugal and Italy.
In England, the feijoa is much appreciated as a wall shrub, though it flowers profusely only in sunny locations. Planting of feijoas has been officially discouraged in New South Wales and Victoria, Australia, because the fruit is a prime host of the fruit fly.
Varieties
As stated, right at the outset seedlings from different sources showed distinct characteristics. It is reported that a man named H. Hehre of Los Angeles got seeds from Argentina and among the seedlings he raised there was one that seemed superior to the others and was earlier bearing. It became known as the 'Hehre' variety. The fruit is large, slender-pyriform, sometimes curved; yellow-green, with thin skin, finely granular flesh, abundant, very juicy pulp, fairly numerous and larger than ordinary seeds, sweet but not aromatic flavor; seedlings erect, compact, vigorous, with lush foliage but only moderately fruitful. 'Andre' (the original air-layer from Brazil), has a medium to large, oblong to round fruit, rough-surfaced, light-green, thick-fleshed, few-seeded; richly flavored and very aromatic. Seedlings are upright, spreading to intermediate. Self-fertile; bears heavily. Besson' (seeds from Uruguay in 1899) has small to medium, oval, smooth fruits with red or maroon cheek; thin-skinned, with medium-thick, fine-grained flesh, very juicy pulp, numerous seeds, and rich, aromatic flavor. Seedlings are upright or spreading. This is the type grown in southern India. Both 'Andre' and 'Besson' have long been prominent in France. 'Coolidge', most commonly grown in California, has fruit varying from pyriform to oblong or elongated, of medium size, with somewhat crinkled skin. It is of indifferent flavor but is a dependable bearer being 100% self-fertile. The plant is upright and strong growing. 'Choiceana', next in favor, has round to oval, fairly smooth, medium sized to small fruit, 2 to 3 1/2 in (5-9 cm) long, of good flavor; almost always or no less than 42% self-fertile; the plant of spreading habit and medium vigor. 'Superba' has round to slightly oval, medium smooth, medium to small fruits of good flavor; it is partially (33%) self-incompatible. The plant is spreading, straggly in habit and of medium vigor.
The two leading New Zealand cultivars are selections made there from 'Choiceana' seedlings: 'Triumph' has oval, short, plump fruits, not as pointed as those of 'Coolidge'; medium to large; smooth. The plant is upright, of medium vigor. 'Mammoth' has oval fruits resembling those of 'Coolidge'; large, to 8 1/2 oz (240 g); somewhat wrinkled. The plant is of upright habit, and strong-growing. In 1979, 'Mammoth', 'Coolidge', and 'Triumph' grown from cuttings were being advertised in the New Zealand journal of Agriculture as suitable for export.
Two new New Zealand cultivars, of which 20,000 plants had been sold in 1983, are 'Apollo', with thin skin subject to bruising and purpling; and 'Gemini', having very small fruits with thin skin. The Association recommends that growers plant the tried and true 'Triumph'.
Among Australian selections are 'Large Oval' and 'Chapman'. 'David' has round or oval fruits with skin of sweet and agreeable flavor; matures in November in Europe. 'Roundjon' has oval or rounded fruits, somewhat rough-skinned and red-blushed; of agreeable flavor; matures in November in Europe. 'Magnifica' is a selected seedling with very large fruits of inferior quality. 'Robert' has oval fruits with grainy flesh, and undesirable brownish leaves. 'Hirschvogel' is highly self-incompatible. 'Bliss' is partially self-incompatible.
The botanical variety variegata has variegated foliage.
Pollination
It has been said that feijoa pollen is transferred by birds that are attracted to and eat the flowers, but bees are the chief pollinators. Most flowers pollinated with compatible pollen show 60 to 90% fruit-set. Hand-pollination is nearly 100% effective. One should plant 2 or more bushes together for cross-pollination unless the cultivar is known to be self-compatible. Poor bearing is usually the result of inadequate pollination.
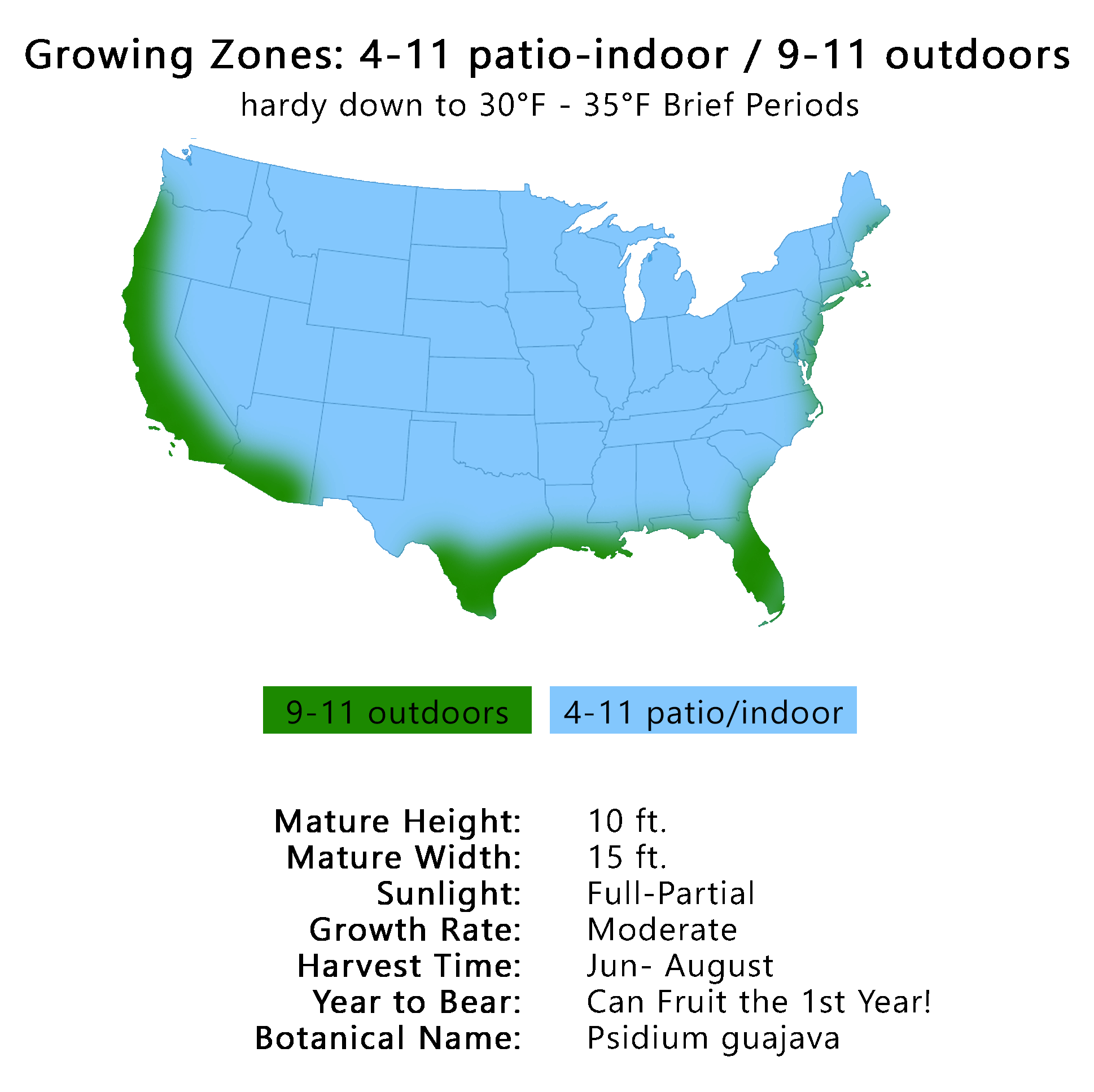
Climate
The feijoa needs a subtropical climate with low humidity. The optimum annual rainfall is 30 to 40 in (762-1,016 mm). The plant thrives where the weather is cool part of the year and it can withstand temperatures as low as 12º to 15º F.The flavor of the fruit is much better in cool than in warm regions.
Soil
While the shrub is often said to be adapted to a wide range of soil types and in England does well even where there is a high chalk content, it actually prefers rich organic soil and is not very thrifty on light or sandy terrain. Some believe that an acid soil is best but the feijoa has done well on soil with a pH of 6.2. It is drought-resistant but needs adequate water for fruit production. The site must be well-drained. The feijoa can tolerate partial shade and slight exposure to salt spray.
Propagation
The feijoa is generally grown from seed and reproduces fairly, but not absolutely, true to type. Seeds are separated by squeezing the seedy pulp into a container, covering with water, and letting the liquid stand for 4 days to ferment. Seeds are then strained out and dried before sowing. The seeds will retain viability for a year or more if kept dry. Germination takes place in 3 weeks. Soil in nursery flats must be sterile, otherwise there will be much loss of seedlings from damping-off. The young plants are transplanted to pots when they have produced their second leaves and later transferred to the field without difficulty. The plant fruits in 3 to 5 years from seed. To reproduce a special selection, vegetative propagation is, of course, necessary. In France and New Zealand-ground-layering is practiced and rooting occurs in 6 months. Air-layering is usually successful and the layers will fruit the second year.
Whip-, tongue-, and veneer-grafting on own rootstock the thickness of a pencil (about 2 years old) gives a low percentage of "takes" but grafted plants will bear in 2 years. Feijoa cuttings are said to be hard to root, but in England and Auckland cuttings are preferred. Young wood from branch tips will root in 1 to 2 months with bottom heat. If placed in sand in a glass-covered box in full sun and kept well watered, they will root in 10 days. In New Zealand, growers are advised to take 4 to 6 in cuttings of side shoots in late summer, cutting close to the firm base or pulling off with a heel of older wood which is then trimmed off; and a hormone rooting agent is applied.
Culture
A 20-year-old plant on the Riviera was reported to be 15 ft (4.5 m) high and 18 ft (5.5 m) in diameter with a trunk 8 in (20 cm.) thick at the base. Because of the spreading habit of such types, 15 to 18 ft (4.5-5.5 m) should be allowed between plants for good fruit production. As the fruit is borne on young wood, pruning reduces the crop, but all shoots below 12 in (30 cm) from the ground should be removed. Some seedlings have a more erect habit and these should be chosen where space is limited. The shrubs may be set 5 ft (1.5 m) apart to form a barrier hedge; 3 ft (1 m) apart in a compact foundation planting. A 15 x 15 ft (4.5 x 4.5 m) spacing requires 190 plants per acre (468 per hectare).
The feijoa requires little care beyond good soil preparation before planting. Subsequent cultivation is inadvisable because of the plant's shallow, fibrous root system which should be left undisturbed. If planted for its fruit, fertilizer should be low in nitrogen to avoid excessive vegetative growth. It should be watered liberally during hot, dry spells.
Season And Yield
Flowering occurs in November in Uruguay, in late April in northern Florida, May in southern California, early June in the San Francisco Bay area and July in England. In southern California the fruits ripen 4 1/2 to 6 months after flowers appear, in the San Francisco Bay area, 5 1/2 to 7 months. In New Zealand fruits are borne from early February to May. The fruits fall when mature and are collected daily from the ground and kept cool until slightly soft to the touch. Straw mulch beneath the plants helps avoid bruising. If picked from the tree before they are ready to fall or if eaten before they are fully ripe, the fruits will not have their full richness of flavor.
The 20-year-old Riviera plant referred to above is said to have borne a crop of 2,000 fruits. The yield is poor in India where the maximum crop per season is 100 fruits per plant, probably due to inadequate pollination or flower damage by birds.
New Zealand test plantings have given the following yields: 3rd year, 13.2 lbs (6 kg) per plant; 4,000 lbs/ acre, (4,000 kg/ha); 4th year, 26.5 lbs (12 kg) per plant; 8,000 lbs/acre, (8,000 kg/ha); 5th year, 39.7 lbs (18 kg) per plant; 12,000 lbs/acre (12,000 kg/ha). The growers now foresee 66 lbs (30 kg) per plant–25 tons per hectare. In 1978, New Zealand produced 333 tons of feijoas–149 tons to be sold fresh, and 184 tons to be processed.
In New Zealand, flat tomato boxes are employed for shipping feijoas. A case 4 1/2 in (11.25 cm) deep and 12 in (30 cm) to 16 in (40 cm) long and wide holds about 20 lbs (9.07 kg).
Keeping Quality
If the atmosphere is too warm, the interior of the fruit turns brown and decays in 3 to 4 days even though the fruit may appear intact on the surface. In cool storage, undamaged fruits will remain in good condition for one month or longer. In France, fruits harvested in November and December have been kept till spring at a cool temperature and with sufficient humidity. In the early days of its introduction, feijoa shipments were successfully made from France to California despite being 30 days at sea. Today, air transport is essential for New Zealand feijoas en route to Europe. They can be held 1 mo at 32º F (0º C) and then have only a week's life on the market.
Pests and Diseases
The shrub is remarkably pest-resistant. Occasionally it may be attacked by hard wax scale (Ceroplastes sinensis) and associated sooty mold in New Zealand and Florida, also greedy scale in New Zealand, by black scale (Saissetia oleae) in California and southern Europe. In New Zealand, the larvae of a leaf-rolling caterpillar (Tortrix spp.)and of a bagworm moth may eat holes in the leaves but they are effectively controlled with suitable sprays. Fruit flies attack the ripe fruits. A leaf-spotting fungus (Sphaceloma sp.) occasionally requires control measures. In Florida, leaf spot is caused by the fungi Cercospora sp., Cylindrocladium scoparium, and Phyllosticta sp.; algal leaf spot by Cephaleuros virescens. Thread blight (Corticium stevensii Burt. and Rhizoctonia ramicola), and mushroom root rot (Clytocybe tabescens).
Food Uses
When preparing feijoas for eating or preserving, peeling should be immediately followed by dipping into a weak salt solution or into water containing fresh lemon juice. Both of these methods will prevent the flesh from oxidizing (turning brown). The flesh and pulp (with seeds) are eaten raw as dessert or in salads, or are cooked in puddings, pastry fillings, fritters, dumplings, fruit-sponge-cake, pies or tarts, or employed as flavoring for ice cream or soft drinks. Surplus fruits may be peeled, halved and preserved in sirup in glass jars, or sliced and crystallized, or made into chutney, jam, jelly, conserve, relish, sauce or sparkling wine.
The thick petals are spicy and are eaten fresh by children and sometimes by adults. The petals may be plucked without interfering with fruit set.
Food Value Per 100 g of Edible Portion*
Moisture84%
Protein
0.9%
Fat
0.2%
Carbohydrates*
10%
Ash
0.5%
Minerals:
Potassium
166 mg
Sodium
5 mg
Calcium
4 mg
Magnesium
8 mg
Phosphorus
10 mg
Iron
0.05 mg
Ascorbic Acid
28-35 mg
*Analyses reported in the literature.
**Sugar 6% compared to 13% in the orange.
The fruit is rich in water-soluble iodine compounds. The percentage varies with locality and from year to year but the usual range is 1.65 to 3.90 mg/kg of fresh fruit. Most types are high in pectin, so that 3 lbs (1.4 kg) of jelly can be made from 1 lb (.45 kg) of fruit. - Features
weight: 9.99 lbs : - ReviewsThere is no reviews yet...Be the first!
Be the first to write a review of this product!













