- Overview
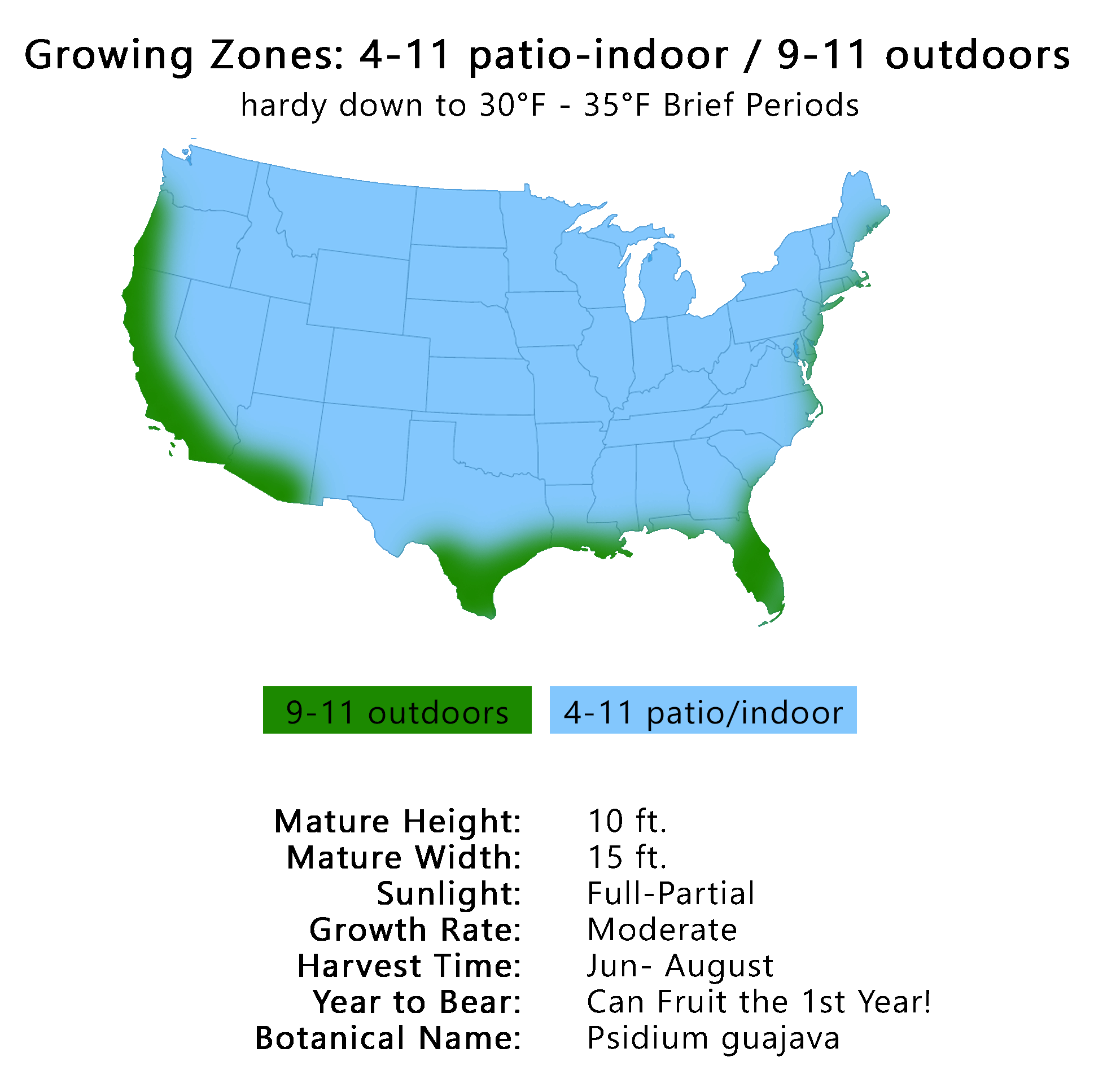
Common name: Guava Botanical name: Psidium guajava Family: Myrtaceae Avg Height X Width: 15' x 15' Origin: Tropical America Season: year round Damage temp: 25-26 F Guava Tree White Variety in a 3 Gallon Container. Guava is enjoyed in jelly, juice, pastries and a multitude of other recipes. The fruit can be round to pear shaped, and they are typically about the size of a baseball. The pulp is smooth, sweet, and extremely aromatic. The trees are heavy producers, and will begin fruiting at just one year of age. Great addition to any garden since the tree fruits year round producing a lot of fruit. Guava's can also be mixed in drinks and smoothies for an amazing flavor.
Description
Origin and Distribution
Cultivars
Pollination
Climate
Soil
Propagation
Culture
Cropping and Yield
Handling and Keeping Quality
Pests and Diseases
Food Uses
Food Value
Other Uses
Medicinal UsesOne of the most gregarious of fruit trees, the guava, Psidium guajava L., of the myrtle family (Myrtaceae), is almost universally known by its common English name or its equivalent in other languages. In Spanish, the tree is guayabo, or guayavo, the fruit guayaba or guyava. The French call it goyave or goyavier; the Dutch, guyaba, goeajaaba; the Surinamese, guave or goejaba; and the Portuguese, goiaba or goaibeira. Hawaiians call it guava or kuawa. In Guam it is abas. In Malaya, it is generally known either as guava or jambu batu, but has also numerous dialectal names as it does in India, tropical Africa and the Philippines where the corruption, bayabas, is often applied. Various tribal names–pichi, posh, enandi, etc.–are employed among the Indians of Mexico and Central and South America.
Description
A small tree to 33 ft (10 in) high, with spreading branches, the guava is easy to recognize because of its smooth, thin, copper-colored bark that flakes off, showing the greenish layer beneath; and also because of the attractive, "bony" aspect of its trunk which may in time attain a diameter of 10 in (25 cm). Young twigs are quadrangular and downy. The leaves, aromatic when crushed, are evergreen, opposite, short-petioled, oval or oblong-elliptic, somewhat irregular in outline; 2 3/4 to 6 in (7-15 cm) long, I 'A to 2 in (3-5 cm) wide, leathery, with conspicuous parallel veins, and more or less downy on the underside. Faintly fragrant, the white flowers, borne singly or in small clusters in the leaf axils, are 1 in (2.5 cm) wide, with 4 or 5 white petals which are quickly shed, and a prominent tuft of perhaps 250 white stamens tipped with pale-yellow anthers. The fruit, exuding a strong, sweet, musky odor when ripe, may be round, ovoid, or pear-shaped, 2 to 4 in (5-10 cm) long, with 4 or 5 protruding floral remnants (sepals) at the apex; and thin, light-yellow skin, frequently blushed with pink. Next to the skin is a layer of somewhat granular flesh, 1/8 to 1/2 in (3-12.5 mm) thick, white, yellowish, light- or dark-pink, or near-red, juicy, acid, subacid, or sweet and flavorful. The central pulp, concolorous or slightly darker in tone, is juicy and normally filled with very hard, yellowish seeds, 1/8 in (3 min) long, though some rare types have soft, chewable seeds. Actual seed counts have ranged from 112 to 535 but some guavas are seedless or nearly so. When immature and until a very short time before ripening, the fruit is green, hard, gummy within and very astringent.
Origin and Distribution
The guava has been cultivated and distributed by man, by birds, and sundry 4-footed animals for so long that its place of origin is uncertain, but it is believed to be an area extending from southern Mexico into or through Central America. It is common throughout all warm areas of tropical America and in the West Indies (since 1526), the Bahamas, Bermuda and southern Florida where it was reportedly introduced in 1847 and was common over more than half the State by 1886. Early Spanish and Portuguese colonizers were quick to carry it from the New World to the East Indies and Guam. It was soon adopted as a crop in Asia and in warm parts of Africa. Egyptians have grown it for a long time and it may have traveled from Egypt to Palestine. It is occasionally seen in Algeria and on the Mediterranean coast of France. In India, guava cultivation has been estimated at 125,327 acres (50,720 ha) yielding 27,319 tons annually. Apparently it did not arrive in Hawaii until the early 1800's. Now it occurs throughout the Pacific islands. Generally, it is a home fruit tree or planted in small groves, except in India where it is a major commercial resource. A guava research and improvement program was launched by the government of Colombia in 1961. In 1968, it was estimated that there were about 10 million wild trees (around Santander, Boyacá, Antioquia, Palmira, Buga, Cali and Cartago) bearing, 88 lbs (40 kg) each per year and that only 10% of the fruit was being utilized in processing. Bogotà absorbs 40% of the production and preserved products are exported to markets in Venezuela and Panama. Brazil's modern guava industry is based on seeds of an Australian selection grown in the botanical garden of the Sao Paulo Railway Company at Tatu. Plantations were developed by Japanese farmers at Itaquera and this has become the leading guava-producing area in Brazil. The guava is one of the leading fruits of Mexico where the annual crop from 36,447 acres (14,750 ha) of seedling trees totals 192,850 tons (175,500 MT). Only in recent years has there been a research program designed to evaluate and select superior types for vegetative propagation and large-scale cultivation. In Florida, the first commercial guava planting was established around 1912 in Palma Sola. Others appeared at Punta Gorda and Opalocka. A 40-acre (16 ha) guava grove was planted by Miami Fruit Industries at Indian-town in 1946. There have been more than two dozen guava jelly manufacturers throughout the state. A Sarasota concern was processing 250 bushels of guavas per day and a Pinellas County processor was operating a 150-bushel capacity plant in 1946. There has always been a steady market for guava products in Florida and the demand has increased in recent years with the influx of Caribbean and Latin American people. The guava succumbs to frost in California except in a few favorable locations. Even if summers are too cool–a mean of 60º F (15.56º C)–in the coastal southern part of the state, the tree will die back and it cannot stand the intense daytime heat of interior valleys. In many parts of the world, the guava runs wild and forms extensive thickets–called "guayabales" in Spanish–and it overruns pastures, fields and roadsides so vigorously in Hawaii, Malaysia, New Caledonia, Fiji, the U.S. Virgin Islands, Puerto Rico, Cuba and southern Florida that it is classed as a noxious weed subject to eradication. Nevertheless, wild guavas have constituted the bulk of the commercial supply. In 1972, Hawaii processed, for domestic use and export, more than 2,500 tons (2,274 MT) of guavas, over 90% from wild trees. During the period of high demand in World War II, the wild guava crop in Cuba was said to be 10,000 tons (9,000 MT), and over 6,500 tons (6,000 MT) of guava products were exported.
Cultivars
Formerly, round and pear-shaped guavas were considered separate species–P. pomiferum L. and P. pyriferum L.–but they are now recognized as mere variations. Small, sour guavas predominate in the wild and are valued for processing.
Pollination
The chief pollinator of guavas is the honeybee (Apis mellifera). The amount of cross-pollination ranges from 25.7 to 41.3%.
Climate
The guava thrives in both humid and dry climates. In India, it flourishes up to an altitude of 3,280 ft (1,000 m); in Jamaica, up to 3,906 ft (1,200 m); in Costa Rica, to 4,590 ft (1,400 m); in Ecuador, to 7,540 ft (2,300 m). It can survive only a few degrees of frost. Young trees have been damaged or killed in cold spells at Allahabad, India, in California and in Florida. Older trees, killed to the ground, have sent up new shoots which fruited 2 years later. The guava requires an annual rainfall between 40 and 80 in (1,000-2,000 mm); is said to bear more heavily in areas with a distinct winter season than in the deep Tropics.
Soil
The guava seems indiscriminate as to soil, doing equally well on heavy clay, marl, light sand, gravel bars near streams, or on limestone; and tolerating a pH range from 4.5 to 9.4. It is somewhat salt-resistant. Good drainage is recommended but guavas are seen growing spontaneously on land with a high water table–too wet for most other fruit trees.
Propagation
Guava seeds remain viable for many months. They often germinate in 2 to 3 weeks but may take as long as 8 weeks. Pretreatment with sulfuric acid, or boiling for 5 minutes, or soaking for 2 weeks, will hasten germination. Seedlings are transplanted when 2 to 30 in (5-75 cm) high and set out in the field when 1 or 2 years old. Inasmuch as guava trees cannot be depended upon to come true from seed, vegetative propagation is widely practiced. In Hawaii, India and elsewhere, the tree has been grown from root cuttings. Pieces of any roots except the smallest and the very large, cut into 5 to 10 in (12.5-20 cm) lengths, are placed flat in a prepared bed and covered with 2 to 4 in (5-10 cm) of soil which must be kept moist. Or one can merely cut through roots in the ground 2 to 3 ft (0.6-0.9 m) away from the tree trunk; the cut ends will sprout and can be dug up and transplanted. By another method, air-layers of selected clones are allowed to grow 3 to 5 years and are then sawn off close to the ground. Then a ring of bark is removed from each new shoot; root-inducing chemical is applied. Ten days later, the shoots are banked with soil to a height 4 to 5 in (10-12.5 cm) above the ring. After 2 months, the shoots are separated and planted out. Pruned branches may serve as propagating material. Cuttings of half-ripened wood, 1/4 to 1/2 in (6-12.5 mm) thick will root with bottom heat or rooting-hormone treatment. Using both, 87% success has been achieved. Treated softwood cuttings will also root well in intermittent mist. In Trinidad, softwood, treated cuttings have been rooted in 18 days in coconut fiber dust or sand in shaded bins sprayed 2 or 3 times daily to keep humidity above 90%. Over 100,000 plants were produced by this method over a 2-year period. Under tropical conditions (high heat and high humidity), mature wood 3/4 to 1 in (2-2.5 cm) thick and 1 1/2 to 2 ft (45-60 cm) long, stuck into 1-ft (30-cm) high black plastic bags filled with soil, readily roots without chemical treatment. In India, air-layering and inarching have been practiced for many years. However, trees grown from cuttings or air-layers have no taproot and are apt to be blown down in the first 2 or 3 years. For this reason, budding and grafting are preferred. Approach grafting yields 85 to 95% success. Trials have been made of the shield, patch and Forkert methods of budding. The latter always gives the best results (88 to 100%). Vigorous seedlings 1/2 to 1 in (1.25-2.5 cm) thick are used as rootstocks. The bark should slip easily to facilitate insertion of the bud, which is then tightly bound in place with a plastic strip and the rootstock is beheaded, leaving only 6 to 8 leaves above the bud. About a month later, an incision is made halfway through 2 or 3 in (5-7.5 cm) above the bud and the plant is bent over to force the bud to grow. When the bud has put up several inches of growth, the top of the rootstock is cut off immediately above the bud. Sprouting of the bud is expedited in the rainy season. At the Horticultural Experiment and Training Center, Basti, India, a system of patch budding has been demonstrated as commercially feasible. A swollen but unsprouted, dormant bud is taken as a 3/4 x 3/8 in (2 x l cm) patch from a leaf axil of previous season's growth and taped onto a space of the same size cut 6 to 8 in (15-20 cm) above the ground on a 1-year-old, pencil-thick seedling during the period April-June. After the bud has "taken", 1/3 is cut from the top of the seedling; 2-3 weeks later, the rest of the top is cut off leaving only 3/4 to 1 1/4 in (2-3.2 cm) of stem above the bud. This method gives 80 to 90% success. If done in July, only 70%. In Hawaii, old seedling orchards have been topworked to superior selections by patch budding on stump shoots.
Culture
Guava trees are frequently planted too close. Optimum distance between the trees should be at least 33 ft (10 m). Planting 16 1/2 ft (5 m) apart is possible if the trees are "hedged". The yield per tree will be less but the total yield per land area will be higher than at the wider spacing. Some recommend setting the trees 8 ft (2.4 m) apart in rows 24 ft (7.3 m) apart and removing every other tree as soon as there is overcrowding. Where mass production is not desired and space is limited, guava trees can be grown as cordons on a wire fence. Rows should always run north and south so that each tree receives the maximum sunlight. Exudates from the roots of guava trees tend to inhibit the growth of weeds over the root system. Light pruning is always recommended to develop a strong framework, and suckers should also be eliminated around the base. Experimental heading-back has increased yield in some cultivars in Puerto Rico. In Palestine, the trees are cut back to 6 1/2 ft (2 m) every other spring to facilitate harvesting without ladders. Fruits are borne by new shoots from mature wood. If trees bear too heavily, the branches may break. Therefore, thinning is recommended and results in larger fruits. Guava trees grow rapidly and fruit in 2 to 4 years from seed. They live 30 to 40 years but productivity declines after the 15th year. Orchards may be rejuvenated by drastic pruning. The tree is drought-tolerant but in dry regions lack of irrigation during the period of fruit development will cause the fruits to be deficient in size. In areas receiving only 15 to 20 in (38-50 cm) rainfall annually, the guava will benefit from an additional 2,460 cm (2 acre feet) applied by means of 8 to 10 irrigations, one every 15-20 days in summer and one each month in winter. Guava trees respond to a complete fertilizer mix applied once a month during the first year and every other month the second year (except from mid-November to mid-January) at the rate of 8 oz (227 g) per tree initially with a gradual increase to 24 oz (680 g) by the end of the second year. Nutritional sprays providing copper and zinc are recommended thrice annually for the first 2 years and once a year thereafter. In India, flavor and quality of guavas has been somewhat improved by spraying the foliage with an aqueous solution of potassium sulfate weekly for 7 weeks after fruit set.
Cropping and Yield
The fruit matures 90 to 150 days after flowering. Generally, there are 2 crops per year in southern Puerto Rico; the heaviest, with small fruits, in late summer and early fall; another, with larger fruits, in late winter and early spring. In northern India, the main crop ripens in mid-winter and the fruits are of the best quality. A second crop is home in the rainy season but the fruits are less abundant and watery. Growers usually withhold irrigation after December or January or root-prune the trees in order to avoid a second crop. The trees will shed many leaves and any fruits set will drop. An average winter crop in northern India is about 450 fruits per tree. Trees may bear only 100-300 fruits in the rainy season but the price is higher because of relative scarcity despite the lower quality. Of course, yields vary with the cultivar and cultural treatment. Experiments have shown that spraying young guava trees with 25% urea plus a wetting agent will bring them into production early and shorten the harvest period from the usual 15 weeks to 4 weeks.
Handling and Keeping Quality
Ripe guavas bruise easily and are highly perishable. Fruits for processing may be harvested by mechanical tree-shakers and plastic nets. For fresh marketing and shipping, the fruits must be clipped when full grown but underripe, and handled with great care. After grading for size, the fruits should be wrapped individually in tissue and packed in 1 to 4 padded layers with extra padding on top before the cover is put on. They have been successully shipped from Miami to wholesalers in major northern cities in refrigerated trucks at temperatures of 45º to 55º F (7.22º-12.78º C). It is commonly said that guavas must be tree-ripened to attain prime quality, but the cost of protecting the crop from birds makes early picking necessary. It has been demonstrated that fruits picked when yellow-green and artificially ripened for 6 days in straw at room temperature developed superior color and sugar content. Guavas kept at room temperature in India are normally overripe and mealy by the 6th day, but if wrapped in pliofilm will keep in good condition for 9 days. In cold storage, pliofilm-wrapped fruits remain unchanged for more than 12 days. Wrapping checks weight loss and preserves glossiness. Unwrapped 'Safeda' guavas, just turned yellow, have kept well for 4 weeks in cold storage at 47º to 50º F (8.33º-10º C) and relative humidity of 85-95%, and were in good condition for 3 days thereafter at room temperature of 76º to 87º F (24º-44º C). Fruits coated with a 3% wax emulsion will keep well for 8 days at 72º to 86º F (22.2º-30º C) and 40 to 60% relative humidity, and for 21 days at 47º to 50º F (8.3º-10º C) and relative humidity of 85-90%. Storage life of mature green guavas is prolonged at 68º F (20º C), relative humidity of 85%, less than 10% carbon dioxide, and complete removal of ethylene. Researchers at Kurukshetra University, India, have shown that treatment of harvested guavas with 100 ppm morphactin (chlorflurenol methyl ester 74050) increases the storage life of guavas by controlling fungal decay, and reducing loss of color, weight, sugars, ascorbic acid and non-volatile organic acids. Combined fungicidal and double-wax coating has increased marketability by 30 days. Australian workers report prolonged life and reduced rotting in storage after a hot water dip, but better results were achieved by dipping in an aqueous benomyl suspension at 122º F (50º C). Higher temperatures cause some skin injury, as does a guazatine dip which is also a less effective fungicide. Fruits sprayed on the tree with gibberellic acid 20-35 days before normal ripening, were retarded nearly a week as compared with the untreated fruits. Also, mature guavas soaked in gibberellic acid off the tree showed a prolonged storage life. Trials at Haryana Agricultural University, Hissar, India, showed that weekly spraying with 1.0% potassium sulfate–1.6 gals (6 liters) per tree–beginning 7 days after fruit set and ending just before harvesting at the pale-green stage, delays yellowing, retains firmness and flavor beyond normal storage life. Food technologists in India found that bottled guava juice (strained from sliced guavas boiled 35 minutes), preserved with 700 ppm SO2, lost much ascorbic acid but little pectin when stored for 3 months without refrigeration, and it made perfectly set jelly.
Pests and Diseases
Guava trees are seriously damaged by the citrus flat mite, Brevipa1pus californicus in Egypt. In India, the tree is attacked by 80 insect species, including 3 bark-eating caterpillars (Indarbella spp.) and the guava scale, but this and other scale insects are generally kept under control by their natural enemies. The green shield scale, Pulvinaria psidii, requires chemical measures in Florida, as does the guava white fly, Trialeurodes floridensis, and a weevil, Anthonomus irroratus, which bores holes in the newly forming fruits. The red-banded thrips feed on leaves and the fruit surface. In India, cockchafer beetles feed on the leaves at the end of the rainy season and their grubs, hatched in the soil, attack the roots. The larvae of the guava shoot borer penetrates the tender twigs, killing the shoots. Sometimes aphids are prevalent, sucking the sap from the underside of the leaves of new shoots and excreting honeydew on which sooty mold develops. The guava fruit worm, Argyresthia eugeniella, invisibly infiltrates hard green fruits, and the citron plant bug, Theognis gonagia, the yellow beetle, Costalimaita ferruginea, and the fruit-sucking bug, Helopeltis antonii, feed on ripe fruits. A false spider mite, Brevipalpus phoenicis, causes surface russeting beginning when the fruits are half-grown. Fruit russeting and defoliation result also from infestations of red-banded thrips, Selenothrips rubrocinctus. The coconut mealybug, Pseudococcus nipae, has been a serious problem in Puerto Rico but has been effectively combatted by the introduction of its parasitic enemy, Pseudaphycus utilis. Soil-inhabiting white grubs require plowing-in of an approved and effective pesticide during field preparation in Puerto Rico. There are other minor pests, but the great problems wherever the guava is grown are fruit flies. The guava is a prime host of the Mediterranean, Oriental, Mexican, and Caribbean fruit flies, and the melon fly–Ceratitis capitata, Dacus dorsalis, Anastrepha ludens, A. suspensa, and Dacus cucurbitae. Ripe fruits will be found infested with the larvae and totally unusable except as feed for cattle and swine. To avoid fruit fly damage, fruits must be picked before full maturity and this requires harvesting at least 3 times a week. In Brazil, choice, undamaged guavas are produced by covering the fruits with paper sacks when young (the size of an olive). Infested fruits should be burned or otherwise destroyed. In recent years, the Cooperative Extension Service in Dade County, Florida, has distributed wasps that attack the larvae and pupae of the Caribbean fruit fly and have somewhat reduced the menace. In Puerto Rico, up to 50% of the guava crop (mainly from wild trees) may be ruined by the uncontrollable fungus, Glomerella cingulata, which mummifies and blackens immature fruits and rots mature fruits. Diplodia natalensis may similarly affect 40% of the crop on some trees in South India. Fruits punctured by insects are subject to mucor rot (caused by the fungus, Mucor hiemalis) in Hawaii. On some trees, 80% of the mature green fruits may be ruined. Algal spotting of leaves and fruits (caused by Cephaleuros virescens) occurs in some cultivars in humid southern Florida but can be controlled with copper fungicides. During the rainy season in India, and the Province of Sancti Spiritus, Cuba, the fungus, Phytophthora parasitica, is responsible for much infectious fruit rot. Botryodiplodia sp. and Dothiorella sp. cause stem-end rot in fruits damaged during harvesting. Macrophomina sp. has been linked to fruit rot in Venezuela and Gliocladium roseum has been identified on rotting fruits on the market in India. In Bahia, Brazil, severe deficiency symptoms of guava trees was attributed to nematodes and nematicide treatment of the soil in a circle 3 ft (0.9 in) out from the base restored the trees to normal in 5 months. Zinc deficiency may be conspicuous when the guava is grown on light soils. It is corrected by two summer sprayings 60 days apart with zinc sulphate. Wilt, associated with the fungi Fusarium solani and Macrophomina phaseoli, brings about gradual decline and death of undernourished 1-to 5-year-old guava trees in West Bengal. A wilt disease brought about by the wound parasite, Myxosporium psidii, causes the death of many guava trees, especially in summer, throughout Taiwan. Wilt is also caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. psidii which invades the trunk and roots through tunnels bored by the larvae of Coelosterna beetles. Anthracnose (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides) may attack the fruits in the rainy season. Pestalotia psidii sometimes causes canker on green guavas in India and rots fruits in storage. Severe losses are occasioned in India by birds and bats and some efforts are made to protect the crop by nets or noisemakers.
Food Uses
Raw guavas are eaten out-of-hand, but are preferred seeded and served sliced as dessert or in salads. More commonly, the fruit is cooked and cooking eliminates the strong odor. A standard dessert throughout Latin America and the Spanish-speaking islands of the West Indies is stewed guava shells (cascos de guayaba), that is, guava halves with the central seed pulp removed, strained and added to the shells while cooking to enrich the sirup. The canned product is widely sold and the shells can also be quick-frozen. They are often served with cream cheese. Sometimes guavas are canned whole or cut in half without seed removal. Bars of thick, rich guava paste and guava cheese are staple sweets, and guava jelly is almost universally marketed. Guava juice, made by boiling sliced, unseeded guavas and straining, is much used in Hawaii in punch and ice cream sodas. A clear guava juice with all the ascorbic acid and other properties undamaged by excessive heat, is made in South Africa by trimming and mincing guavas, mixing with a natural fungal enzyme (now available under various trade names), letting stand for 18 hours at 120º to 130º F (49º-54º C) and filtering. It is made into sirup for use on waffles, ice cream, puddings and in milkshakes. Guava juice and nectar are among the numerous popular canned or bottled fruit beverages of the Caribbean area. After washing and trimming of the floral remnants, whole guavas in sirup or merely sprinkled with sugar can be put into plastic bags and quick-frozen. There are innumerable recipes for utilizing guavas in pies, cakes, puddings, sauce, ice cream, jam, butter, marmalade, chutney, relish, catsup, and other products. In India, discoloration in canned guavas has been overcome by adding 0.06% citric acid and 0.125% ascorbic acid to the sirup. For pink sherbet, French researchers recommend 2 parts of the cultivar 'Acid Speer' and 6 parts 'Stone'. For white or pale-yellow sherbet, 2 parts 'Supreme' and 4 parts 'Large White'. In South Africa, a baby-food manufacturer markets a guava-tapioca product, and a guava extract prepared from small and overripe fruits is used as an ascorbic-acid enrichment for soft drinks and various foods. Dehydrated guavas may be reduced to a powder which can be used to flavor ice cream, confections and fruit juices, or boiled with sugar to make jelly, or utilized as pectin to make jelly of low-pectin fruits. India finds it practical to dehydrate guavas during the seasonal glut for jelly-manufacture in the off-season. In 1947, Hawaii began sea shipment of frozen guava juice and puree in 5-gallon cans to processors on the mainland of the United States. Since 1975, Brazil has been exporting large quantities of guava paste, concentrated guava pulp, and guava shells not only to the United States but to Europe, the Middle East, Africa and Japan. Canned, frozen guava nectar is an important product in Hawaii and Puerto Rico but may be excessively gritty unless stone cells from the outer flesh and skin are reduced by use of a stone mill or removed by centrifuging. In South Africa, guavas are mixed with cornmeal and other ingredients to make breakfast-food flakes. Green mature guavas can be utilized as a source of pectin, yielding somewhat more and higher quality pectin than ripe fruits.
Food Value Per 100 g of Edible Portion (Flesh)*
Calories 36-50
Moisture 77-86 g
Crude Fiber 2.8-5.5 g
Protein 0.9-1.0 g
Fat 0.1-0.5 g
Ash 0.43-0.7 g
Carbohydrates 9.5-10 g
Calcium 9.1-17 mg
Phosphorus 17.8-30 mg
Iron 0.30-0.70 mg
Carotene (Vitamin A) 200-400 I.U.
Thiamine 0.046 mg
Riboflavin 0.03-0.04 mg
Niacin 0.6-1.068 mg
Vitamin B3 40 I.U.
Vitamin G4 35 I.U.
*Analyses of whole ripe guavas.
Ascorbic acid–mainly in the skin, secondly in the firm flesh, and little in the central pulp–varies from 56 to 600 mg. It may range up to 350-450 mg in nearly ripe fruit. When specimens of the same lot of fruits are fully ripe and soft, it may decline to 50-100 mg. Canning or other heat processing destroys about 50% of the ascorbic acid. Guava powder containing 2,500-3,000 mg ascorbic acid was commonly added to military rations in World War II. Guava seeds contain 14% of an aromatic oil, 15% protein and 13% starch. The strong odor of the fruit is attributed to carbonyl compounds.
Other Uses
Wood: The wood is yellow to reddish, fine-grained, compact, moderately strong, weighs 650-750 kg per cubic meter; is durable indoors; used in carpentry and turnery. Though it may warp on seasoning, it is much in demand in Malaya for handles; in India, it is valued for engravings. Guatemalans use guava wood to make spinning tops, and in El Salvador it is fashioned into hair combs which are perishable when wet. It is good fuelwood. and also a source of charcoal.
Leaves and bark: The leaves and bark are rich in tannin (10% in the leaves on a dry weight basis, 11-30% in the bark). The bark is used in Central America for tanning hides. Malayans use the leaves with other plant materials to make a black dye for silk. In southeast Asia, the leaves are employed to give a black color to cotton; and in Indonesia, they serve to dye matting.
Wood flowers: In Mexico, the tree may be parasitized by the mistletoe, Psittacanthus calyculatus Don, producing the rosette-like malformations called "wood flowers" which are sold as ornamental curiosities.
Medicinal_Uses
The roots, bark, leaves and immature fruits, because of their astringency, are commonly employed to halt gastroenteritis, diarrhea and dysentery, throughout the tropics. Crushed leaves are applied on wounds, ulcers and rheumatic places, and leaves are chewed to relieve toothache. The leaf decoction is taken as a remedy for coughs, throat and chest ailments, gargled to relieve oral ulcers and inflamed gums; and also taken as an emmenagogue and vermifuge, and treatment for leucorrhea. It has been effective in halting vomiting and diarrhea in cholera patients. It is also applied on skin diseases. A decoction of the new shoots is taken as a febrifuge. The leaf infusion is prescribed in India in cerebral ailments, nephritis and cachexia. An extract is given in epilepsy and chorea and a tincture is rubbed on the spine of children in convulsions. A combined decoction of leaves and bark is given to expel the placenta after childbirth. The leaves, in addition to tannin, possess essential oil containing the sesquiterpene hydrocarbons caryophyllene, b-bisabolene, aromadendrene, b-selinene, nerolidiol, caryophyllene oxide and sel-11-en-4x -ol, also some triterpenoids and b-sitosterol. The bark contains tannin, crystals of calcium oxalate, ellagic acid and starch. The young fruits are rich in tannin. - Features
weight: 9.99 lbs : - ReviewsThere is no reviews yet...Be the first!
Be the first to write a review of this product!











